The REACT EO4SDG Mini Project Winners
The REACT Technical Committee of the IEEE GRSS is proud to announce the winner of the 2023 EO4SDG Mini Projects contest.
Several projects have been submitted from different countries with great ideas and contribution related to the sustainable development goals using remote sensing techniques and tools.
As before, this year’s contest was judged by the REACT Technical Committee team:
Prof. Irena Hajnsek from ETH Zürich and German Aerospace Center, Dr. Carlos Lopez Martinez from the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, and Prof. Avik Bhattacharya for the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay.
We want to thank all of the entrants to this year’s contest! It has been an honor to witness each of your work.
We are pleased to share the winning team and the content of their proposal.
We like to congratulate the winners:
Divyeshkumar Rana and Hanieh Dadkhah
Department of Earth Sciences
Sapienza Università di Roma, Rome, Italy
Title of the proposal submitted:
‘Infrastructure Monitoring using Persistent Scatterer Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PS-InSAR) Technique for Ravenna City, Italy’
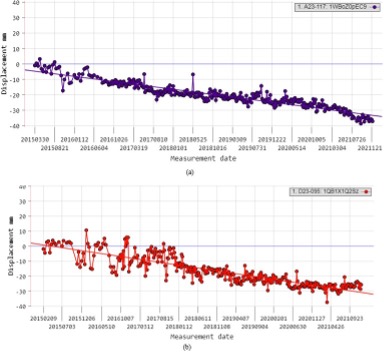
Infrastructure monitoring is essential for ensuring the safety of the public, preventing costly repairs, optimizing resource allocation, meeting regulatory standards, and adapting to the challenges posed by natural disasters and climate change. It ultimately leads to more sustainable, efficient, and resilient infrastructure systems. Persistent Scatterer Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PS-InSAR or PSI) is a remote sensing technique used to monitor ground movements with high precision over time. It utilizes radar waves from satellites to measure the phase difference between multiple radar images acquired over the same area. Certain stable radar reflectors on the Earth’s surface, called persistent scatterers, provide consistent signals across multiple images, enabling the detection of ground displacement. PS-
InSAR is particularly valuable in infrastructure monitoring, where it can detect and monitor subsidence, settlement, deformation, and other ground movements. It has various applications, including monitoring bridges, dams, tunnels, pipelines, landslides, and urban infrastructure. By providing detailed information about ground stability, PS-InSAR helps in the early detection of potential issues, aiding in disaster prevention, urban planning, and infrastructure maintenance. Geological understanding plays an important role in understanding Beneath the alluvial deposits, there are layers of sediments and rocks, including clay, sand, and gravel. These subsurface geological formations contribute to the hydrogeological characteristics of the region and influence factors such as groundwater flow. Ravenna is located relatively close to the Adriatic Sea. The proximity to the coast means that the area’s geological features are influenced by coastal processes, including the deposition of sediments carried by sea currents.
The results are related to the SDG 11 Sustainable Cities and Communities and are showing an average line of sight (LOS) velocity of -4 mm/year to -5 mm/year with ground deformation of 40 to 45 mm. The analysis was made with Sentinel-1 and are still ongoing. For example, linear infrastructure like roads and railways are to be analyzed thoroughly. Further, a Risk map shall be created to distribute the vulnerable areas caused by subsidence by considering various driving factors.